Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
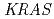 wild-type and
wild-type and 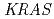 mutant colorectal cancer using
mutant colorectal cancer using  Cu-labeled cetuximab positron emission tomography
Cu-labeled cetuximab positron emission tomographyAchmad, A.*; 花岡 宏史*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 山元 進司*; 富永 英之*; 荒木 拓也*; 大島 康宏; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*
Cancer Science, 103(3), p.600 - 605, 2012/03
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:55.86(Oncology)Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is common in colorectal cancer. However, cetuximab, an EGFR-targeting drug, is useful only for a subset of patients and no single predictor other than V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (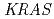 ) mutation status has been established. In this study, we investigated cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors using
) mutation status has been established. In this study, we investigated cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors using  In-DOTA-cetuximab, and evaluated the potential of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of
In-DOTA-cetuximab, and evaluated the potential of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. We found that
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. We found that 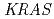 wild-type tumors had significantly higher
wild-type tumors had significantly higher  In-DOTA-cetuximab accumulation than
In-DOTA-cetuximab accumulation than 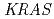 mutant tumors. Based on
mutant tumors. Based on 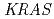 mutation status, a strong correlation was found between
mutation status, a strong correlation was found between  In-DOTA-cetuximab tumor uptake and EGFR expression level. Significant correlation was also found between tumor uptake of
In-DOTA-cetuximab tumor uptake and EGFR expression level. Significant correlation was also found between tumor uptake of  In-DOTA-cetuximab and
In-DOTA-cetuximab and  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. PET imaging with
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. PET imaging with  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab effectively visualized cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors with a wide variety of EGFR expression levels and different
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab effectively visualized cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors with a wide variety of EGFR expression levels and different 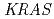 mutation status as commonly encountered in the clinical setting. Our findings suggest that this radioimmunoimaging can be clinically translated as an in vivo tool to predict cetuximab accumulation in colorectal cancer patients prior to cetuximab therapy.
mutation status as commonly encountered in the clinical setting. Our findings suggest that this radioimmunoimaging can be clinically translated as an in vivo tool to predict cetuximab accumulation in colorectal cancer patients prior to cetuximab therapy.
田中 成岳*; 木村 仁*; Faried, A.*; 酒井 真*; 佐野 孝昭*; 猪瀬 崇徳*; 宗田 真*; 岡田 幸士*; 中島 政信*; 宮崎 達也*; et al.
Cancer Science, 101(6), p.1487 - 1492, 2010/06
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:31.77(Oncology)大気マイクロPIXEを用いて、食道ガン細胞株において、主要な化学療法薬であるシスプラチンの細胞内局在性を調べ、同細胞株のシスプラチンに対する感度を決定した。2種類のヒト食道扁平上皮癌(ESCC)細胞株(TE-2とTE-13)のシスプラチンに対する感受性は、MTT分析,フローサイトメトリ、及びDNA断片化分析を用いて確認した。これらの細胞試料に対して大気マイクロPIXE分析を行うとともに、リアルタイム逆転写ポリメラーゼ連鎖反応を用いて両細胞株における、「マルチ-ドラッグ」抵抗性タンパク質2(MRP2)のmRNA発現を評価した。この結果、TE-2セルはTE-13セルよりシスプラチンに敏感であることが明らかとなった。この研究結果は、大気マイクロPIXEが個別細胞のシスプラチン感受性を定量評価する方法として有効であることを示唆した。また、最終的には細胞膜の中のMRP2がESCC細胞のシスプラチン感受性を制御する重要な役割を担っているのではないかという推測に至った。
 Cu-labeled trastuzumab PET
Cu-labeled trastuzumab PETPaudyal, P.*; Paudyal, B.*; 花岡 宏史*; 織内 昇*; 飯田 靖彦*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 富永 英之*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; et al.
Cancer Science, 101(4), p.1045 - 1050, 2010/04
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:66.53(Oncology)Non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) overexpress the Her2/neu gene in approximately 59% of cases. Trastuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, interferes with Her2 signaling and is approved for the treatment of Her2/neu overexpressing breast cancer. However, its therapeutic use in Her2/neu overexpressing NSCLC remains obscure. The present study aimed to determine the role of  Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with
Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
原田 耕作*; 野中 哲生*; 浜田 信行*; 桜井 英幸*; 長谷川 正俊*; 舟山 知夫; 柿崎 竹彦*; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Cancer Science, 100(4), p.684 - 688, 2009/04
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:75.67(Oncology)The aim of the present study was to clarify the mechanisms of cell death induced by heavy-ion irradiation focusing on the bystander effect in human lung cancer A549 cells. In microbeam irradiation, each of 1, 5 and 25 cells under confluent cell conditions was irradiated with 1, 5 or 10 particles of energetic carbon ions, and then the surviving fraction of the population was measured by a clonogenic assay in order to investigate the bystander effect of heavy-ions. In this experiment, the limited number of cells (0.0001-0.002%, 5-25 cells) under confluent cell conditions irradiated with 5 or 10 carbon ions resulted in an exaggerated 8-14% increase in cell death by clonogenic assay. However, these overshooting responses were not observed under exponentially growing cell conditions. Furthermore, these responses were inhibited in cells treated with an inhibitor of gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC), whereas these were markedly enhanced by the addition of a stimulator of GJIC. The present results suggest that bystander cell killing by heavy-ions was induced mainly by direct cell-to-cell communication, such as GJIC, which might play important roles in the bystander responses.